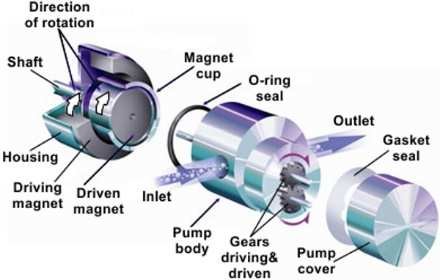
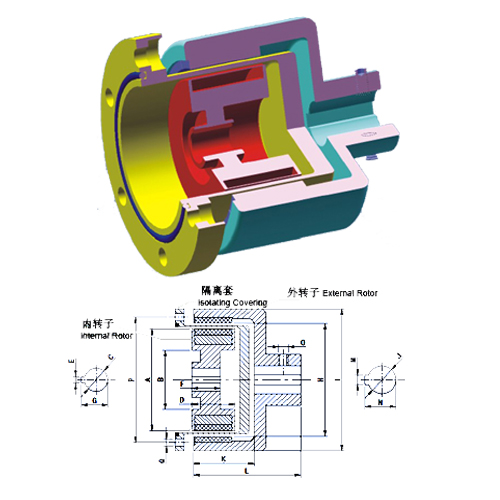
The working principle of magnetic coupling
The working principle of magnetic coupling:
Magnetic drive couplings mainly have two structures: planar magnetic drive couplings and coaxial magnetic drive couplings. The magnet is magnetized in the axial direction, and the coupling magnetic poles are arranged in the axial direction. It is called a plane magnetic drive coupling. The magnet is magnetized in the radial direction, and the coupling magnetic poles are arranged in the radial direction, which is called a coaxial magnetic drive coupling.
Now take the coaxial magnetic drive coupling as an example to illustrate its working principle. The magnetic drive coupling is composed of an outer magnet, an inner magnet and an isolation cover. The inner and outer magnets are both composed of permanent magnets magnetized in the radial direction and magnetized in opposite directions. The permanent magnets are alternately arranged in the circumferential direction with different polarities and are fixed on a low-carbon steel ring to form a magnetically disconnected conjoined body. The isolation cover is made of non-ferritic (hence non-magnetic) high-resistance material, generally austenitic stainless steel. In the static state, the N pole (S pole) of the outer magnet and the S pole (N pole) of the inner magnet attract each other and form a straight line. At this time, the torque is zero. When the outer magnet rotates under the drive of the power machine, the inner magnet is still in a static state due to the friction force and the resistance of the driven parts at the beginning. , The N pole (S pole) of the outer magnet has a pulling effect on the S pole (N pole) of the inner magnet, and the N pole (S pole) of the outer magnet has a push to the previous N pole (S pole) of the inner magnet. The function makes the inner magnet have a tendency to follow the rotation, which is the working principle of the push-pull magnetic circuit of the magnetic coupling. When the N pole (S pole) of the outer magnet is just between the two poles (S pole and N pole) of the inner magnet, the push-pull force generated reaches the maximum, thereby driving the inner magnet to rotate. In the transmission process, the isolation cover separates the outer magnet and the inner magnet, and the magnetic field lines pass through the isolation cover to transmit the power and movement of the outer magnet to the inner magnet, thus realizing a non-contact sealed transmission.