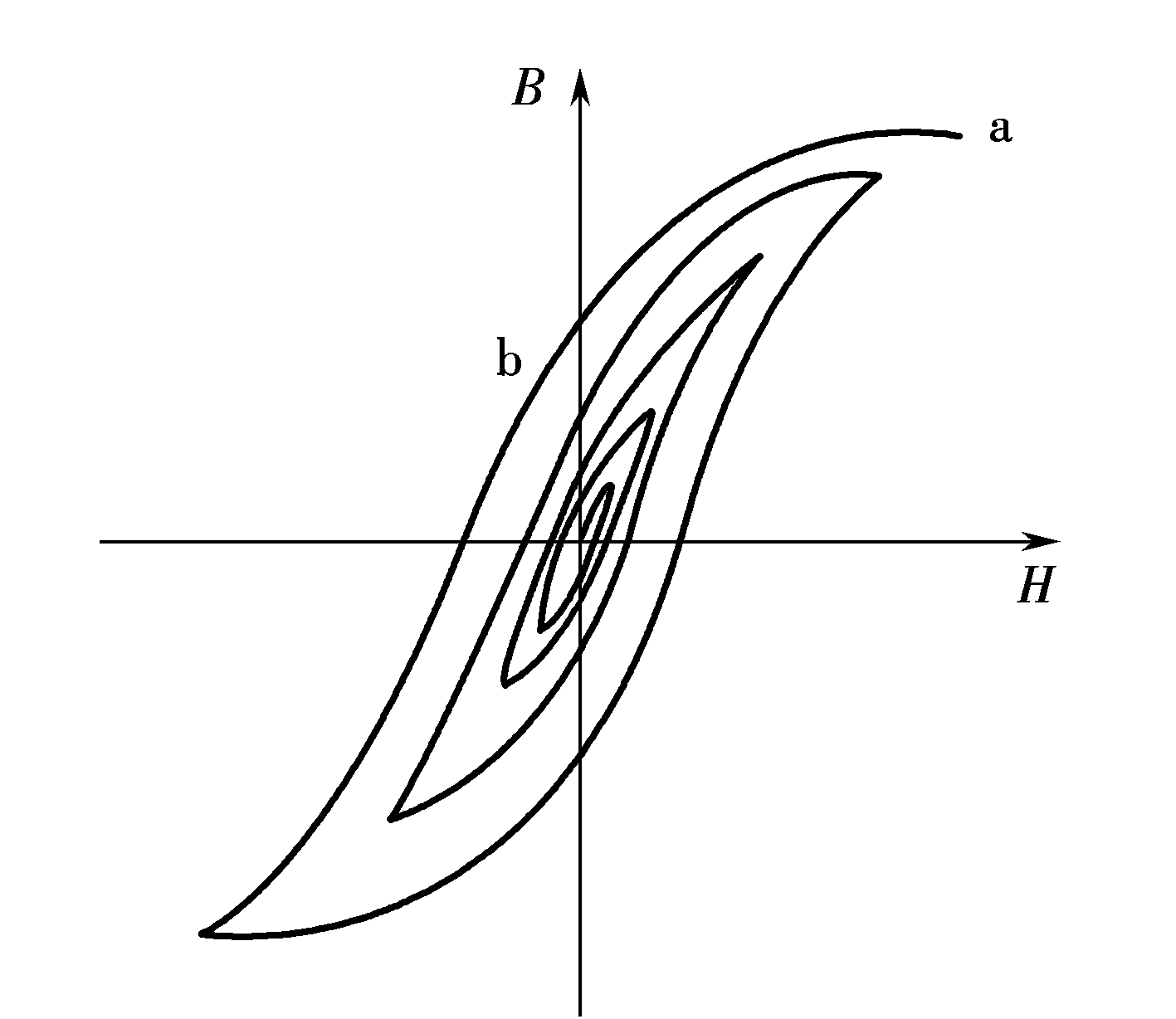
The main parameters of permanent magnet materials
The shape and characteristics of the hysteresis curve of permanent magnetic materials can be expressed by several parameters. In practical applications, the magnetic materials can be classified according to the difference in quantity of these parameters, and their use can be determined. These parameters are also the main factors in the design of magnetic circuits. in accordance with.
1. Saturation magnetic field strength Hm
In the process of magnetization of the magnetic material, the magnetic field intensity that makes the induction intensity B reach the saturation value Bm is called the saturation magnetic field intensity Hm. The magnetic material should be fully magnetized during magnetization, that is, the magnetizing magnetic field intensity H should reach the Hm value in order to obtain the demagnetization curve of the maximum possible magnetization. This kind of demagnetization curve is the most stable and can show the best magnetic properties of the material. If the magnetizing magnetic field intensity H is lower than the Hm value, there will be a hysteresis curve of different shapes, the demagnetization curve will be unstable, and the magnetic performance of the magnet will be low.
It can be seen that the Hm value of the magnetic material used should be known during the production process of the magnetic material, and the magnetic field must reach or exceed this value during the magnetization process.
2. Residual magnetic induction Br
The intersection of the hysteresis curve and the ordinate axis, that is, the B value at the starting point of the demagnetization curve, is called the residual magnetic induction, or remanence for short, and is represented by Br. It is the magnetic induction intensity value of the magnet after the external magnetic field is removed from the magnetic material.
3. Magnetic induction coercivity Hc
Under the action of a negative magnetic field, the magnetic induction intensity B in the magnet decreases with the increase of the demagnetizing magnetic field. The demagnetization magnetic field strength required to make the magnetic induction intensity B in the magnet reach zero is called the magnetic induction coercive force, or coercive force for short, expressed by Hc or Hcb.
4. Magnetic permeability
The slope of any point on the initial magnetization curve and the hysteresis loop, that is, the ratio of the increments of B and H at any point, is called permeability, which varies with the operating point. The magnetic permeability of soft magnetic materials is large, while the magnetic permeability of permanent magnetic materials/hard magnetic materials is small.
Generally speaking, the smaller the ratio of the residual magnetic induction Br to the coercive force Hc, the smaller the magnetic permeability. For permanent magnets, people usually care about the three quantities of initial permeability, maximum permeability and reversible permeability, which will be explained in detail in the near future.
It can be said that the magnetization curve and hysteresis loop are the main basis for the classification and selection of magnetic materials. The following figure shows several common typical hysteresis loops.