Long-term stability of magnets at high temperatures
The figure below shows the relative flux loss of magnets with different Pc values and HcJ=20.1 kOe at 80°C, 120°C and 150°C over time.
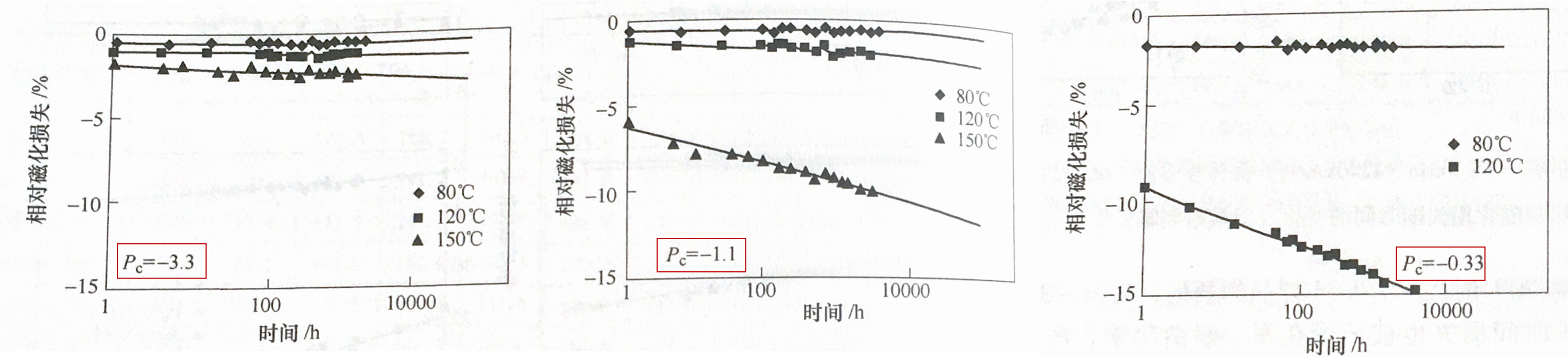
From the above figure, it is not difficult to find that under the same Pc value, the higher the magnet storage temperature, the faster the relative magnetic flux loss will decrease. The initial magnetization loss and long-term magnetization loss of magnets with lower absolute value of Pc are significantly greater than those of magnets with higher Pc, and the two types of losses increase greatly due to temperature rise. In the case that the HcJ cannot be further improved due to technical and cost reasons, the The increase in the absolute value of Pc can effectively suppress the magnetization loss.
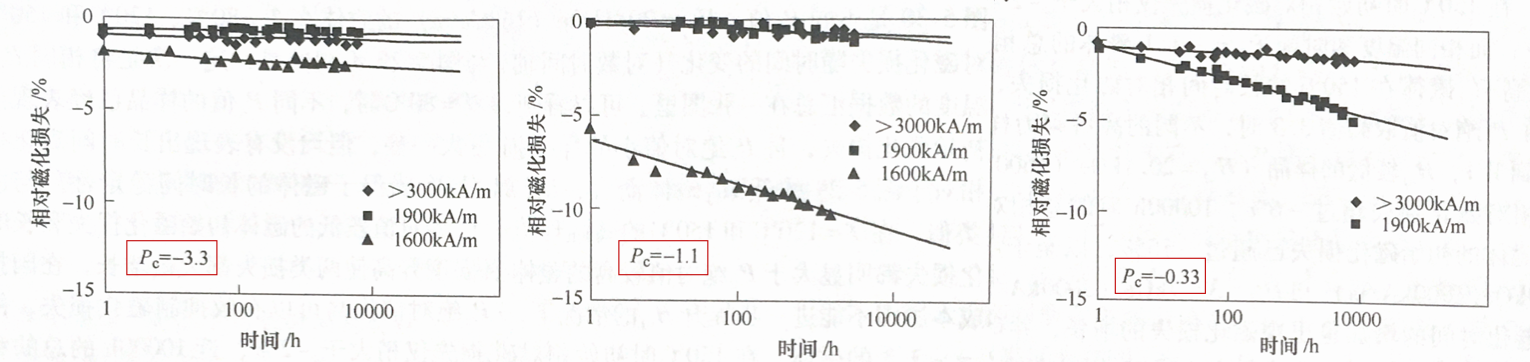
From the time relationship of the relative magnetization loss of different HcJ and different Pc magnets at different temperatures, it can be seen that HcJ has an important influence on the high-temperature magnetization loss. The higher the HcJ, the lower the magnetization loss. The high-temperature stability requires the magnet to have higher HcJ. At the same time, the permeability coefficient Pc can also determine the high-temperature and long-term magnetization loss of the magnet.
If you want to know more about magnets, please click on our website :www.magnet-forever.com
