Effect of Magnet Performance on Speaker Sound Output Quality
Everyone knows that magnets are needed in electro-acoustic equipment such as speakers, stereos, and headphones, so
-What is the role of magnets in electroacoustic devices?
- What effect does the magnet performance have on the sound output quality?
-Which magnet should be used in different quality speakers?
The core component responsible for sound in audio equipment is the speaker, whether it is a speaker or a headset, this key component is indispensable. A speaker is a transducer device that converts electrical signals into acoustic signals. The performance of the speaker has a great influence on the sound quality. If you want to understand speaker magnetism, you must first start with the sound principle of the speaker.
How the speaker works
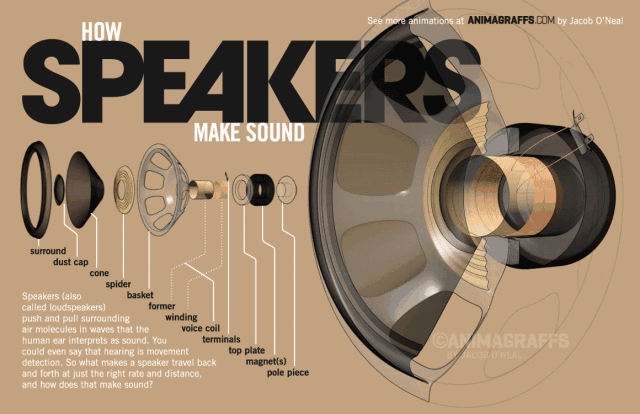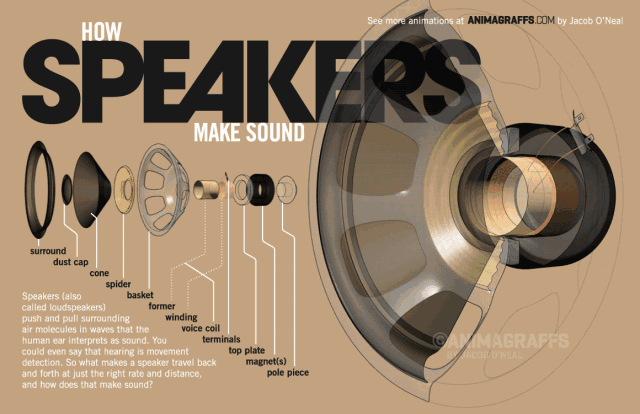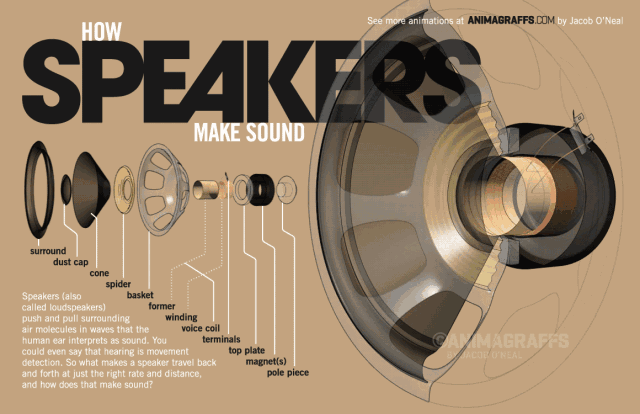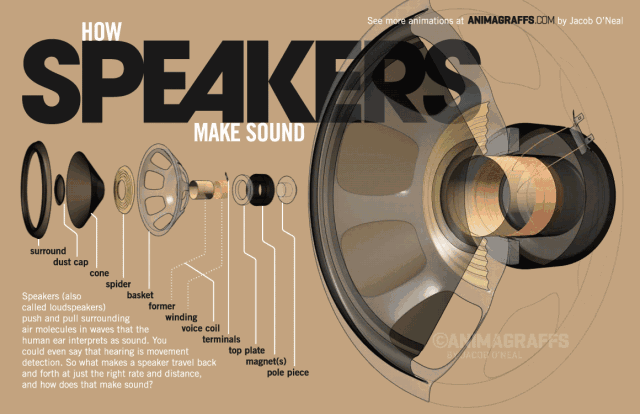
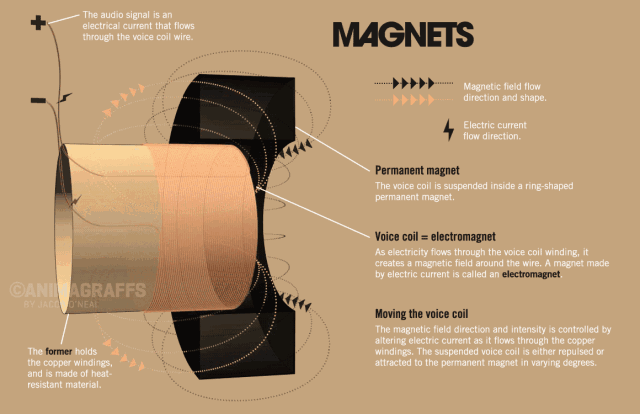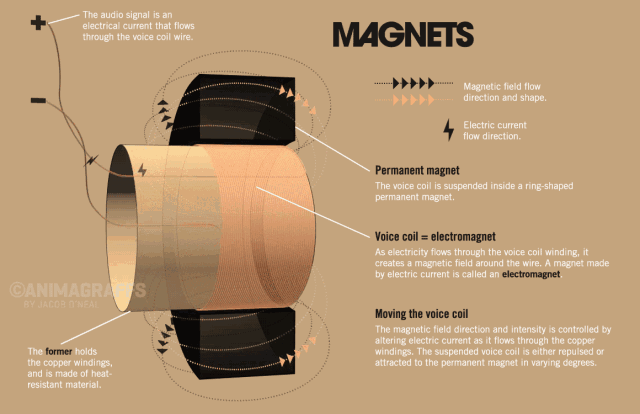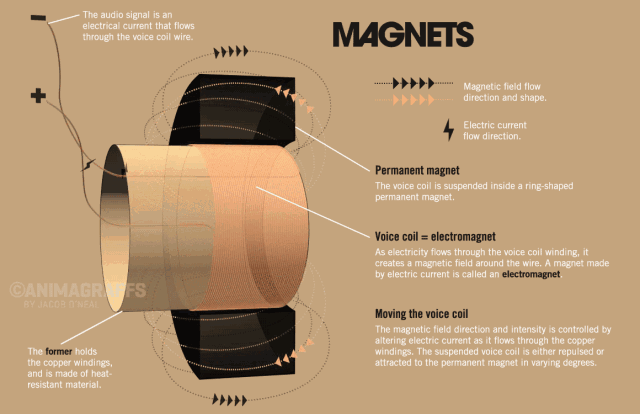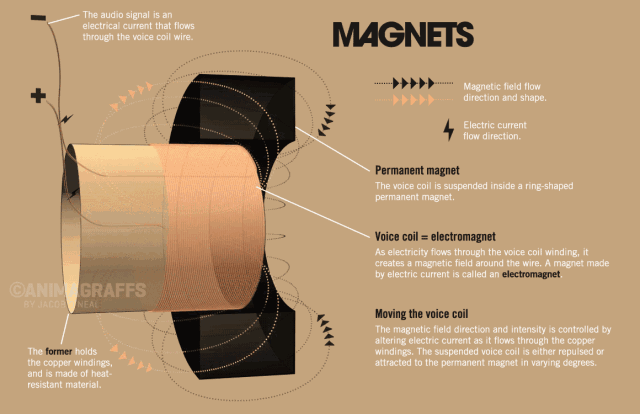
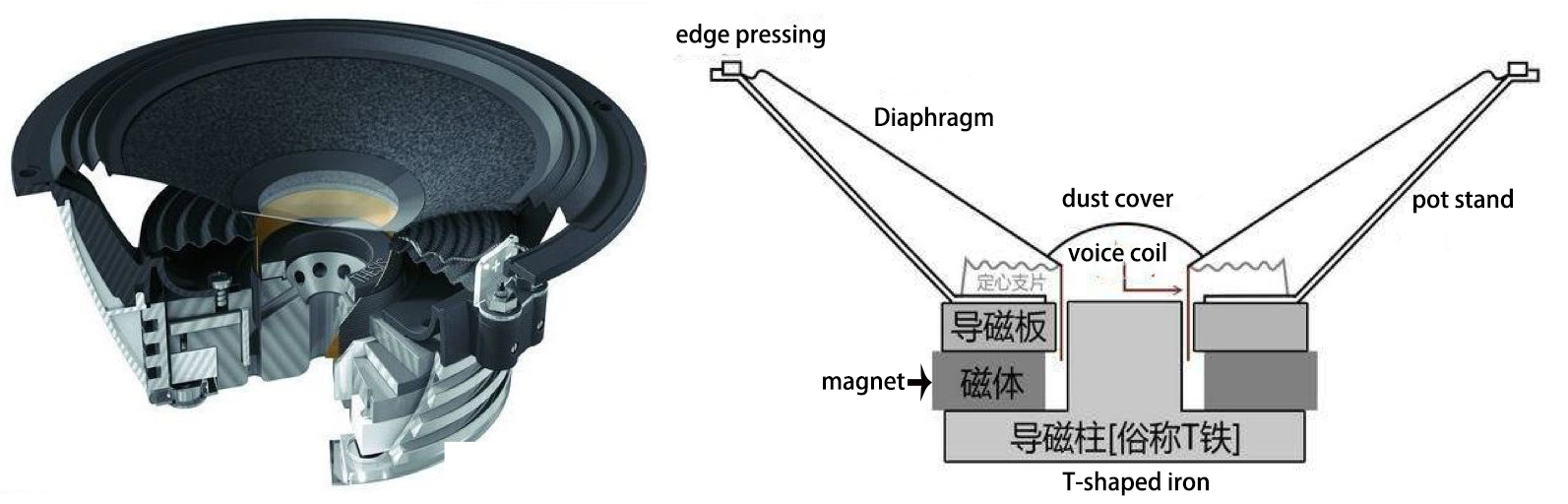
The side view of the speaker below can help us understand the basic structure of the speaker very well. The speaker is generally composed of several key components: T iron, magnet, voice coil and diaphragm.
So how does the speaker sound? We all know that a magnetic field will be generated in the energized wire. The strength of the current affects the strength of the magnetic field (the direction of the magnetic field follows the right-hand rule). When the AC audio current passes through the coil (ie the voice coil) of the speaker, according to the above principle, the voice coil A corresponding magnetic field is generated, and this magnetic field interacts with the magnetic field generated by the built-in magnet on the speaker. This force makes the voice coil vibrate with the strength of the audio current in the magnetic field of the speaker. The diaphragm and voice coil of the speaker are connected together. When the voice coil vibrates with the diaphragm of the speaker, it pushes the surrounding air to vibrate, and the speaker produces sound. As shown below, this is the principle of the speaker.
Effect of Magnet Performance on Speaker Sound Output Quality
In the case of the same magnet volume and the same voice coil, the magnet performance has a direct impact on the sound quality of the speaker:
The greater the magnetic flux density (magnetic induction) B of the magnet, the stronger the thrust acting on the sound membrane.
The larger the magnetic flux density (magnetic induction) B, the higher the power, and the higher the SPL sound pressure level (sensitivity).
The earphone sensitivity is the sound pressure level that the earphone can emit when a sine wave of 1mw and 1khz is input to the earphone. The unit of sound pressure is dB (decibel).
The larger the magnetic flux density (magnetic induction intensity) B, the lower the overall quality factor Q value of the speaker.
The Q value (qualityfactor) refers to a set of parameters of the damping coefficient of the horn, wherein Qms is the damping of the mechanical system, which reflects the energy absorption and consumption of the movement of each component of the horn. Qes is the damping of the power system, which is mainly reflected in the power consumption of the voice coil DC resistance; Qts is the total damping, which is related to the above two as Qts=Qms*Qes/(Qms+Qes).
The larger the magnetic flux density (magnetic induction) B, the better the transient.
Transient can be understood as a "fast response" to the signal, and the Qms is relatively high. Headphones with good transient response should respond immediately as soon as the signal comes, and stop abruptly as soon as the signal stops, and never be sloppy. Such as: especially in the symphony of drums and larger scenes, the transition from lead to ensemble is most obvious.